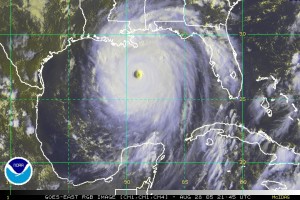
 A Tropical Cyclone – generically describes a low pressure system that typically forms in the tropics. A collection of strong thunderstorms makeup a cyclone, and in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds rotate counterclockwise. In the North Atlantic Ocean, the Northeast Pacific Ocean east of the dateline, or the South Pacific Ocean east of 160E, Tropical cyclones are also called hurricanes, tropical storms, and tropical depressions, depending upon intensity. In different parts of the world these storms have different names such as:
A Tropical Cyclone – generically describes a low pressure system that typically forms in the tropics. A collection of strong thunderstorms makeup a cyclone, and in the Northern Hemisphere, surface winds rotate counterclockwise. In the North Atlantic Ocean, the Northeast Pacific Ocean east of the dateline, or the South Pacific Ocean east of 160E, Tropical cyclones are also called hurricanes, tropical storms, and tropical depressions, depending upon intensity. In different parts of the world these storms have different names such as:
- Typhoon – the Northwest Pacific Ocean west of the dateline
- Severe Tropical Cyclone – the Southwest Pacific Ocean west of 160E or Southeast Indian Ocean east of 90E
- Severe Cyclonic Storm – the North Indian Ocean
- Tropical Cyclone – the Southwest Indian Ocean
Tropical cyclones require warm ocean temperatures, moisture, and light winds as the basic ingredients for storm development. If these conditions last long enough a developing tropical cyclone will become a hurricane, producing violent winds, incredible waves, torrential rains and floods.
The Atlantic hurricane season begins June 1 and ends November 30. The East Pacific hurricane season runs from May 15 through November 30, with peak activity occurring during July through September.